
AmCAT - The Amsterdam Content Analysis Toolkit
So, you have been gathering a huge dataset consisting of continuously retrieved social media posts. But now, you cannot analyze it in your local computer because you do not have a large enough RAM. What should you do?
One possible answer is to upload the data into a server and then perform the analysis from there. But, now that you have done it, you realized that you need and extra skill: “Big Textual Data Handling” ... So, now what?
Well, for both problems, there is one solution AmCAT (Amsterdam Content Analysis Toolkit)!
AmCAT is a software designed to run in a computing server and to facilitate big text data handling and analytics. AmCAT achieves both goals by exploding the power of Elasticsearch and by building a Graphic User Interface (GUI) that allows easy data exploration.
How AmCAT works
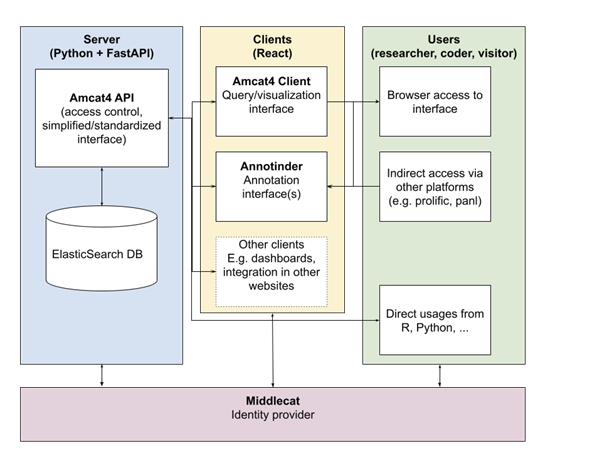
Figure 1: AmCAT-architecture.
As Figure 1 shows, AmCAT relies on Elasticsearch to store and handle the data. Elasticsearch is an opened source software built to speed-up handling and analysis of big unstructured data (Gormley & Tong, 2015). Internally, in short, it works by inverse indexing any given JSON object. A fundamental difference in Elasticsearch is that it is document oriented, meaning that it stores entire objects or documents. It not only stores them, but also indexes the contents of each document in order to make them searchable. In Elasticsearch, you index, search, sort, and filter documents —not rows of columnar data. This is a fundamentally different way of thinking about data and is one of the reasons Elasticsearch (therefore, AmCAT) can perform complex full-text search in seconds.
AmCAT can be accessed through different ways. If you are comfortable using Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), then you can access AmCAT through the Amcat4 API. You can also access the AmCAT API through R and Python. More information on how to access them is in section 2 of the AmCAT book. If you are more comfortable using Graphic User Interfaces (GUIs), then Amcat4 Client is for you. You can check an example of it following this link (Figure 2).
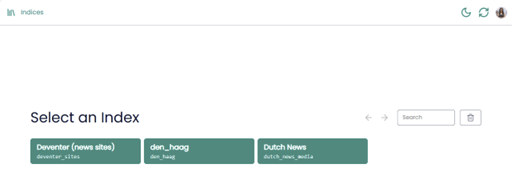
Figure 2: AmCAT Graphic User Interface demo.
AmCAT quick overview through the Graphic User Interface
AmCAT goal is to facilitate and speed-up big textual analytics. It does so by easing access to all Elasticsearch functionalities. In this section, we give a quick overview of some of the things that AmCAT can do. In the examples, we will focus on the GUI, but all can be translated to the API.
As Figure 2 shows, there are already some big textual databases preloaded to this server: Deventer (news site), den_hag, and Dutch News. Each of them can now be accessed through the AmCAT GUI. These databases can now be searched, analysed, and visualized using AmCAT. For example, if we choose the Dutch News database, then we will see something like Figure 3.
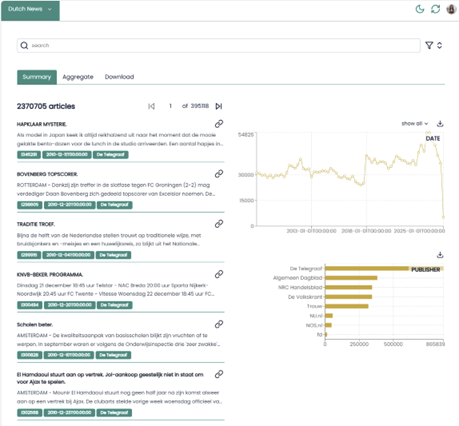
Figure 3: Summary of the Dutch News using AmCAT.
The Summary option gives us access to some basic information of the data. For example, there are 2,370,705 articles in the database. The collection goes from January 1st, 2008, to October 1st, 2024. The Dutch journals that are considered are: The Telegraaf, Algemeen Dagblad, De Volskrant, etc. We can also access the articles’ metadata by clicking on them (Figure 4).
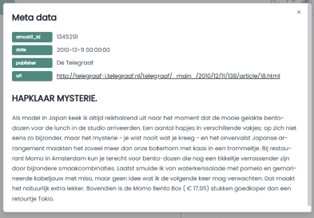
Figure 4: AmCAT metadata example.
Elasticsearch (therefore, AmCAT) main feature is the speed at which searches are done: super fast! This can be tested by looking for some words or phrases using the “look for” section (Figure 5). Figure 5 shows the articles that mentioned “kerstman” (i.e. Santa Claus in Dutch). Similar to Figure 4, the AmCAT also returns a basic summary of the result.
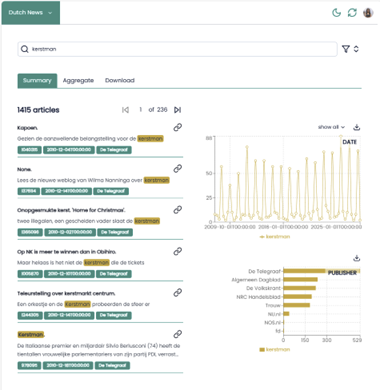
Figure 5 : Result from the search for the word “kerstman”.
The Aggregate option (Figure 6) allows users to analyse and visualize the data in an interactive manner. The GUI gives access to the following visualizations: Line Graph, Bar Chart, List, and Table. In terms of analyses, it only allows to count/aggregate the values, which is already useful to get a quick understanding of the data!
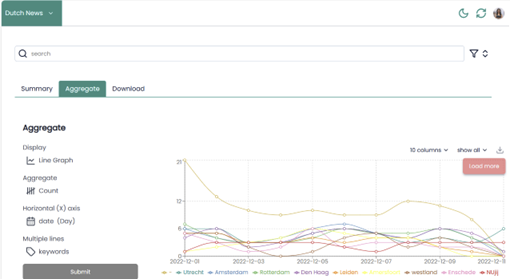
Figure 6: AmCAT Aggregate option applied to the Dutch News database.
References
-
Gormley, C., & Tong, Z. (2015). Elasticsearch: The definitive guide; [a distributed real-time search and analytics engine] (1. ed). O’Reilly.
